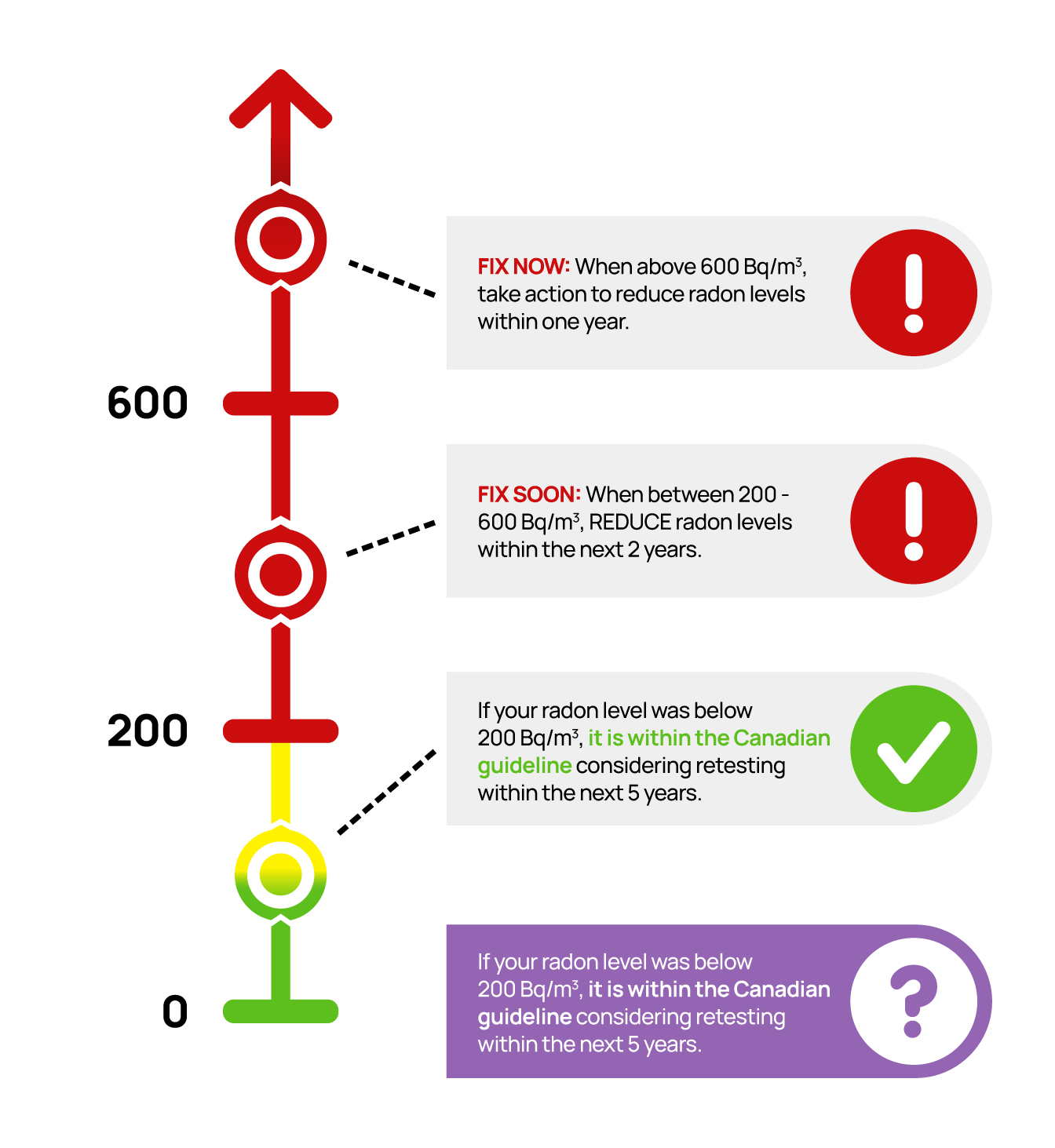
The Canadian guideline for radon in indoor air is 200 Bq/m3.
If you’ve tested your home, and the radon concentration is above the Canadian guideline of 200 Bq/m3, Health Canada recommends that you take action to lower the concentrations.
The higher the radon concentrations, the sooner action should be taken to reduce levels to as low as practically possible.
Health Canada recommends that homeowners consult with a Radon Mitigation Professional certified by the Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program (C-NRPP) to determine the best radon reduction method. While the health risk from radon exposure below the Canadian guideline is small, there is no level that is considered risk free. It is the choice of each homeowner to decide what level of radon exposure they are willing to accept.
When taking steps to reduce your radon levels, Health Canada recommends taking actions that will reduce your radon levels to as low as possible.
According to research the most efficient method of reducing residential radon levels is through installation of an Active Soil Depressurization (ASD) or a radon mitigation system installed by a certified professional.
Additional, but less effective, methods of radon reduction may include sealing cracks or other radon entry routes or increasing ventilation through balancing or installing an HRV (Heat Recovery Ventilator) or ERV (Energy Recovery Ventilator) system. See Health Canada’s ASD study for more information.
Click here for more information on radon reduction for Canadian homeowners.